Google's AI TPUs: The Secret Engine Powering the AI Revolution
The Secret Engine Powering the AI Revolution
You’ve seen the headlines. You’ve interacted with the chatbots. You’ve marveled at AI-generated art and video. Models like Gemini, GPT-4, and Midjourney are not just software; they are computational behemoths. Training them requires a level of processing power that was almost unimaginable a decade ago.
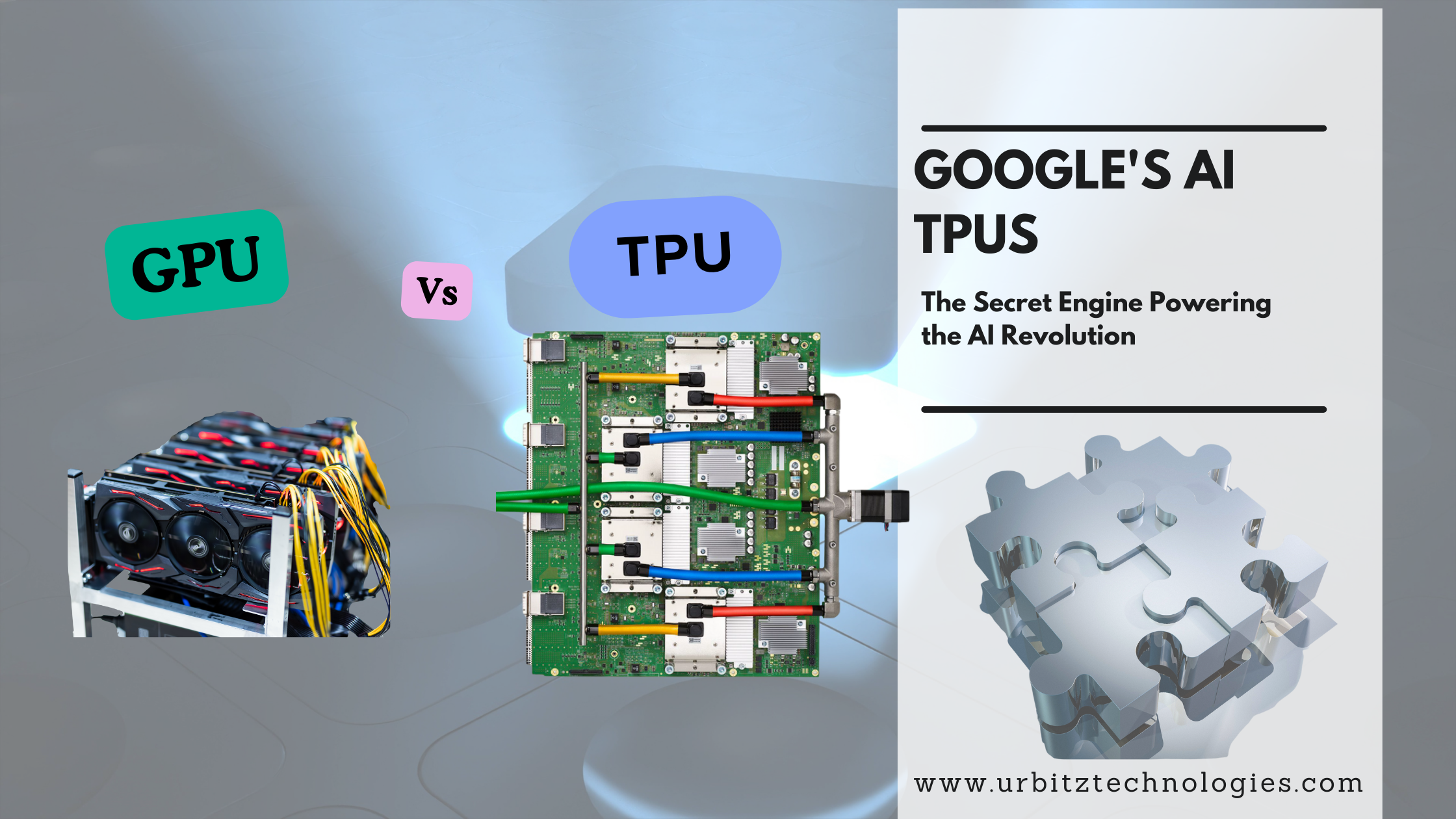
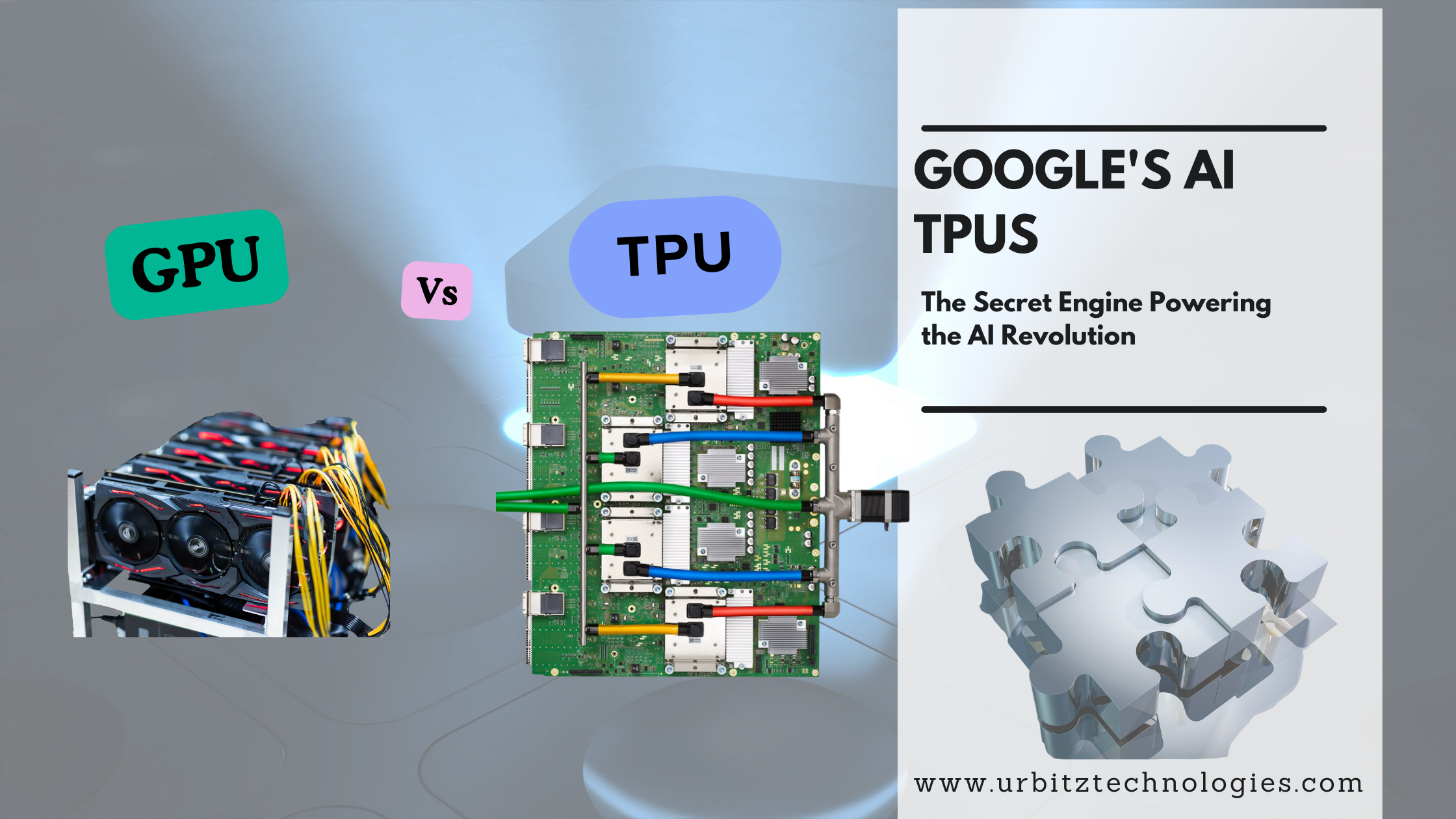
So, what’s powering this revolution? While NVIDIA's GPUs often grab the spotlight, there's a silent, specialized workhorse in the background: Google's Tensor Processing Unit, or TPU.
What if you could build a chip from the ground up, not for graphics or general computing, but for one thing only: accelerating AI? That’s exactly what Google did. Let's dive into the world of TPUs and discover how this custom-built hardware is shaping the future of intelligence.
What is a TPU? The Chef's Knife in a World of Swiss Army Knives
At its core, a TPU is an Application-Specific Integrated Circuit (ASIC). Unlike a CPU (Central Processing Unit) or GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) designed for a wide range of tasks, a TPU is built for a single, critical function: speeding up neural network machine learning.
Think of it this way:
A CPU is like a general-purpose workshop. It can handle any task you throw at it, from calculations to managing files, but it does them one after another, or in a small queue. It's versatile but can be slow for massive, parallel jobs.
A GPU is like a Swiss Army knife with thousands of identical blades. It's fantastic for tasks that can be broken down into thousands of smaller, parallel operations—like rendering pixels for a game or performing the matrix math crucial for AI. It's a powerful, flexible tool.
A TPU, then, is a master chef's knife. It can't open a can or screw in a bolt, but for the specific task of slicing and dicing—or in this case, multiplying and adding matrices—it is unparalleled in its speed and efficiency. It is a specialized instrument designed for a single, crucial domain.
This fundamental architectural difference is the source of the TPU's remarkable power.
Why TPUs? The Core Advantages
So, we know what a TPU is. But why does this approach deliver such a massive performance boost? The answer lies in ruthless specialization.
1. Hardware Designed for Matrices, Not General Tasks
Neural networks run on linear algebra, specifically, operations called matrix multiplications. A CPU handles these operations sequentially. A GPU handles them in parallel, but still has architectural overhead from its graphics-rendering heritage.
A TPU’s entire architecture is a "matrix multiplication engine." It uses a design called a systolic array, which is a network of thousands of multipliers and adders that work in a coordinated rhythm, like a well-conducted orchestra, to perform tens of thousands of operations simultaneously. This massive, dedicated parallelism is the key to its raw speed.
2. The Efficiency King: TOPS/Watt
In the world of large-scale computing, raw speed isn't the only metric that matters—cost and power consumption are paramount. This is measured as "Tera-Operations-Per-Second per Watt" (TOPS/W).
Because TPUs have no unnecessary circuitry for tasks they'll never perform, they deliver vastly more computations for every watt of power consumed compared to a GPU or CPU. For Google, running billions of AI inferences daily across Search, Photos, and Translate, this efficiency translates to millions of dollars in saved energy costs and a significantly reduced carbon footprint. It makes the impossible scale of modern AI economically feasible.
3. A Simplified, High-Bandwidth Memory Architecture
AI models are massive, often with billions of parameters. Keeping this data close to the processors is critical to avoid bottlenecks—a problem known as the "memory wall."
TPUs are designed with a "unified buffer" of high-bandwidth memory placed strategically on the same chip. This allows the processors to access the data they need incredibly quickly, unlike a GPU which might have to fetch data from slower, off-chip memory. Think of it as having your entire kitchen workspace (the memory) within arm's reach of the chef (the processor), rather than having to run to a pantry across the room for every ingredient.
A Brief History of TPUs: From Project to Powerhouse
The TPU story isn't one of an overnight success, but of a long-term strategic bet.
TPU v1 (2015): Born from a necessity for faster AI inference, the first TPU was deployed secretly inside Google's data centers. It famously powered AlphaGo in its historic match against Lee Sedol, providing the computational muscle to evaluate positions with incredible speed.
TPU v2 (2017): This generation added a critical capability: training. Now, Google could not only run AI models but also train them from scratch on this custom hardware, a major leap that cemented the TPU's strategic importance.
TPU v3 (2018) & v4 (2021): The scale exploded. v3 introduced liquid cooling to handle the immense heat. v4 pods, with their innovative optical circuit switching, could be wired together to form supercomputers dedicated to AI, offering exaflops of performance. These pods became the training ground for Google's largest models.
TPU v5e & v5p (2023/2024): The latest generation is built for the era of foundation models. It offers even greater performance and is optimized for both training and serving the most massive models, like Gemini, at unprecedented speed and scale.
How Can You Use TPUs? Democratizing Supercomputing
You might think, "This is great for Google, but what about me?" The incredible part is that this power is accessible.
Through Google Cloud TPU, any developer, researcher, or company can rent access to these same supercomputing pods. The barrier to entry for state-of-the-art AI training has never been lower.
Getting started is surprisingly straightforward, thanks to deep integration with popular AI frameworks:
TensorFlow: The original framework with native TPU support.
PyTorch: Supported via the XLA (Accelerated Linear Algebra) compiler, making the vast PyTorch ecosystem TPU-compatible.
JAX: This is a key point. JAX, a research framework from Google, is particularly well-suited to exploit TPU architecture. Its functional, composable nature maps perfectly onto the TPU's systolic arrays, and it's gaining massive traction in high-performance AI research circles.
Who is using this? AI labs training new LLMs, pharmaceutical companies simulating molecules, and startups running high-throughput inference for their applications. The playing field is being leveled.
The Bigger Picture: TPUs and the AI Ecosystem
It's important to note that TPUs aren't operating in a vacuum. The AI hardware space is a vibrant and competitive arena.
NVIDIA GPUs: The current dominant force, with a mature software ecosystem (CUDA) and incredible performance of their own with chips like the H100 and B200.
AMD GPUs: A strong competitor with their MI300 series, pushing the boundaries of performance.
This competition is healthy and drives innovation. Google's TPU strategy creates a powerful "moat." It allows them to control the entire stack, from the silicon to the software (TensorFlow/JAX) to the end-user applications (Search, Gmail, Gemini). This vertical integration lets them innovate faster and more efficiently than if they were reliant on third-party hardware.
Conclusion: The Future is Built on Specialized Silicon
The story of the TPU is more than just a tale of a fast chip. It signals a fundamental shift in computing. The era of one-size-fits-all processing is giving way to an age of specialized silicon.
As AI models continue to grow in complexity and become more integrated into our daily lives, the hardware they run on will become even more critical. Google's TPU, born from a practical need for speed and efficiency, has evolved into a cornerstone of the modern AI ecosystem. It proves that to unlock the next wave of intelligence, we can't just write better algorithms; we must also build better, smarter computers.
The engine of the AI revolution isn't just code. It's physical. It's specialized. And it's just getting started.
Want to learn more? Check out the Google Cloud TPU documentation to start your own supercomputing journey.
Let us know in the comments: What AI problem would you solve if you had access to a TPU pod?
Could you help with a version for non techy audience
Of course! Here's a version of the blog article written for a non-technical audience, using simple analogies and avoiding jargon.
Google's Secret Sauce for AI: What are TPUs and Why Do They Matter?
You've probably chatted with a helpful AI, seen amazing AI-generated images, or used a tool that seems to magically understand what you want. Behind the scenes, these smart AIs need a special kind of brainpower to learn and work—and it's not the same kind of computer chip that's in your laptop or phone.
Google, a leader in AI, built its own special computer chip just for this job. It's called a Tensor Processing Unit, or TPU. Think of it as a custom-built, high-performance engine designed specifically for the complex work of artificial intelligence.
Let's break down what that means for you and the future of technology.
The Right Tool for the Job: From Kitchen Utensils to Computer Chips
Imagine you're in the kitchen preparing a big meal.
A standard computer chip (a CPU) is like a versatile chef's knife. You can chop vegetables, slice meat, and even use the handle to crack a nut. It's a good all-around tool.
A graphics card chip (a GPU) is like a high-quality food processor. It's fantastic for quickly chopping a huge pile of onions or kneading multiple batches of dough all at once. This makes it great for complex tasks like video games and, as it turns out, many AI tasks.
Google's TPU, however, is like a specialized tomato slicer or avocado pitter. It does one thing, and it does it perfectly. It can't crack a nut, but for slicing tomatoes with incredible speed and precision, nothing can beat it.
For AI, that "one thing" is the core math behind learning and making decisions. By building a chip that is a master of this single task, Google made it incredibly fast and energy-efficient.
Why Does a Special Chip Even Matter?
You might wonder why we can't just use the powerful chips we already have. The answer comes down to two things: speed and efficiency.
Unbeatable Speed for AI Tasks: Training a major AI (like the brain behind a smart chatbot) is an enormous task. Using general-purpose chips would be like trying to win a Formula 1 race with a family minivan. It might eventually get there, but it would take forever. TPUs are the race cars of the AI world, built specifically for this "track," allowing them to train AIs in weeks instead of years.
Saving Massive Amounts of Energy: Running these powerful computers uses a lot of electricity. Because TPUs are so focused on their job, they waste very little energy on tasks they weren't designed to do. They get more "thinking" done per watt of power. For a company like Google that runs AI billions of times a day, this efficiency saves a huge amount of money and is much better for the environment.
A Quick Trip Down Memory Lane: The TPU's Journey
Google didn't just invent TPUs overnight. Their development shows how AI has evolved.
The First TPU (2015): This was the beginning. Google built the first TPU to make its products like Google Search and Photos faster and smarter behind the scenes. It was so effective that it secretly powered the AI (AlphaGo) that beat the world champion at the incredibly complex game of Go.
The Next Generations: Later versions became even more powerful. Google figured out how to use TPUs not just to run AIs, but to teach them in the first place. They started connecting thousands of these chips together to form "supercomputers" dedicated solely to AI, which could train the massive brains behind tools like Google Translate and the Gemini AI.
How Does This Affect You?
This might sound like something only Google uses, but the effects ripple out to all of us.
Better, Smarter Products: The efficiency and power of TPUs are why you can get accurate, real-time translations, find what you're looking for with a quick search, or have a natural conversation with an AI. They help make these services faster, cheaper, and more capable for everyone.
Driving Innovation Forward: Google also rents out access to its TPUs through its cloud service. This means that a small startup or a university researcher can use the same super-powered technology that Google uses. This helps new ideas and amazing new AIs get built by people all over the world, not just by big tech companies.
The Big Picture: A More Specialized Future
Google's TPU is part of a bigger trend in technology. We're moving away from "one-size-fits-all" computer chips and toward building specialized tools for specific jobs, just like a master chef has a kitchen full of specific tools.
While other companies like NVIDIA and AMD make incredibly powerful AI chips too (like the GPUs in food processors), Google's TPU shows the unique power of designing something from the ground up for a single purpose: intelligence.
In a Nutshell
So, the next time you interact with a helpful AI, remember that it's not just smart software. It's likely running on a custom-built brain—a specialized chip like Google's TPU. These chips are the unsung heroes, the powerful engines working behind the scenes to make our technology smarter, faster, and more helpful for everyone.
We hope this helped demystify the tech behind the AI you use every day! What's the most surprising way you've used AI recently? Let us know in the comments






Fabricated Alumimium bracket for wall mounted camera
Cameras supported includes but not limited to :
TP-Link tapo
Imou ranger